This course I’ve specifically crafted for those of you who are at the threshold of cloud technology, aiming to build a robust foundation in Azure’s services, and understanding the core principles that drive security, privacy, compliance, and trust in the cloud environment.
Azure is not just a technology; it’s a new way of thinking. It offers a shift from the traditional on-premises approach to a more dynamic, scalable, and cost-effective model.
For those with an IT background, the concepts we discuss may resonate quickly, but the course is structured to ensure that even if you’re new to the field, you’ll find the learning curve to be smooth and the concepts, approachable.
Let’s begin by setting our intentions for this course. What do you hope to achieve? Whether it’s gaining the knowledge to pass the AZ-900 exam or to make informed decisions about cloud services in your role, keep that goal in mind as we progress. I encourage you to ask questions, engage in discussions, and take part in the exercises we have planned.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the structure of this course and how it will serve as a stepping stone towards your goals in cloud computing.
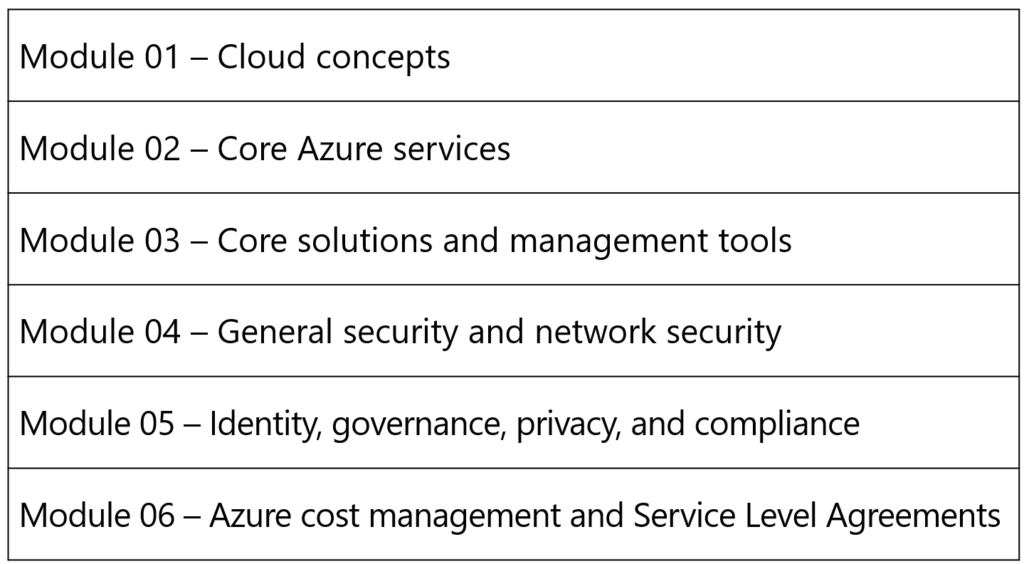
Certification areas (AZ-900)
Cloud Concepts
What is cloud computing?
Let’s ask ourselves, ‘What is cloud computing? What does it truly mean? Cloud computing is not just about storing data or running applications from a remote server. It is about revolutionizing the way we access, consume, and manage technology.
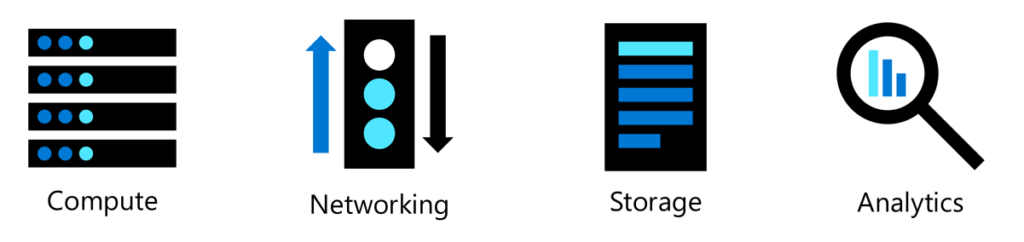
‘Compute’ – this is the raw processing power that can be scaled up or down to handle your applications. ‘Networking’ is the backbone, connecting data centers to users anywhere. ‘Storage’ is where we keep our data safe and accessible. And ‘Analytics’ – this is where all our data turns into insights that drive business decisions.
But why use the cloud? It’s not just for the innovation or flexibility; it’s also for price. Cloud providers like Azure can offer lower costs because resources are shared across numerous users.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
What is Azure?
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/intro-to-azure-fundamentals/what-is-microsoft-azure
Tour of Azure Services
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/intro-to-azure-fundamentals/tour-of-azure-services
Get started with Azure accounts
Case study introduction
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/intro-to-azure-fundamentals/case-study-introduction
Public cloud is a platform where computing services are offered by cloud service providers over the public internet and are available to anyone who wants to purchase them. It’s owned and operated by providers like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon, offering unparalleled resources and services to organizations and users globally. This is where you can tap into advanced services like machine learning, analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities without the need for significant capital investment. It’s all about making powerful tools available to everyone.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/fundamental-azure-concepts/types-of-cloud-computing
Private cloud is a dedicated cloud infrastructure operated only for a single organization. It may be managed internally or by a third party, and hosted either on-premises or off. This model provides the same scalability and efficiency of the public. The private cloud is often chosen by organizations with strict regulatory requirements, sensitive data, or unique business needs that public clouds can’t meet as precisely. Unlike the public cloud, where resources are shared among various tenants, the private cloud is like having an exclusive highway for your organization’s traffic – you dictate the rules, the speed, and the direction. Remember, the choice between public and private clouds is not always clear-cut. It depends on a variety of factors including cost, compliance, scalability, and specific business needs.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/fundamental-azure-concepts/types-of-cloud-computing
Hybrid cloud is a model that combines the public and private clouds.
Why hybrid? Because it offers the best of both worlds. The hybrid cloud allows businesses to store protected or privileged data on a private cloud, while still taking advantage of the power of a massive public cloud for everyday data processing.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/fundamental-azure-concepts/types-of-cloud-computing
Cloud model comparison
| Public Cloud | No capital expenditures to scale up. Applications can be quickly provisioned and de-provisioned. Organizations pay only for what they use. |
| Private Cloud | Hardware must be purchased for start-up and maintenance. Organizations have complete control over resources and security. Organizations are responsible for hardware maintenance and updates. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Provides the most flexibility. Organizations determine where to run their applications. Organizations control security, compliance, or legal requirements. |
Learn and SkillPipe content:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/fundamental-azure-concepts/types-of-cloud-computing
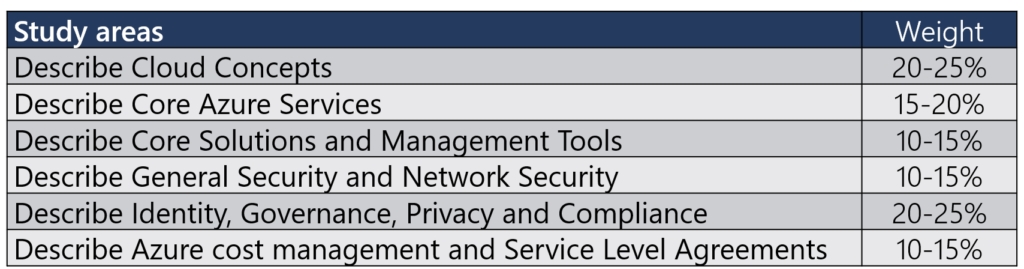
Cloud Benefits – Objective Domain
Let’s talk a little bit about benefits of cloud computing, the distinctions between Capital Expenditure (CapEx) and Operational Expenditure (OpEx), and the concept of the consumption-based model. These concepts form the bedrock of understanding cloud services, making them essential for your professional development in the world of technology.
Key benefits of cloud computing
1. High Availability: Cloud computing offers unparalleled high availability, ensuring that your applications and data are accessible 24/7. This is achieved through redundant infrastructure, geographically dispersed data centers, and advanced load balancing, resulting in minimal downtime and enhanced reliability.
2. Scalability: Cloud services allow you to scale your resources up or down according to your business needs. This flexibility is essential for handling traffic spikes, accommodating growth, and optimizing resource utilization, ultimately leading to cost savings.
3. Elasticity: Elasticity takes scalability a step further by automatically adjusting resources in real-time based on demand. This ensures that you pay only for the resources you actually use, eliminating the need for over-provisioning and reducing waste.
4. Agility: Cloud computing promotes agility by enabling rapid deployment and resource provisioning. With cloud services, you can quickly experiment, innovate, and respond to changing market conditions, giving your organization a competitive edge.
5. Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery solutions, including data replication, backup, and fail over capabilities. These features ensure that your data is secure and can be recovered quickly.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
Compare CapEx vs. OpEx
Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
The up-front spending of money on physical infrastructure.
Costs from CapEx have a value that reduces over time.
Operational Expenditure (OpEx)
Spend on products and services as needed, pay-as-you-go
Get billed immediately
Learn and SkillPipe content:
Consumption-Based Model: The consumption-based model, also known as pay-as-you-go or pay-per-use, is a fundamental principle of cloud computing. It means that you are charged based on your actual usage of cloud resources. This model offers cost efficiency, as you only pay for what you consume, with the ability to scale up or down as needed. It aligns costs with actual usage patterns, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking to optimize their IT expenditure.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
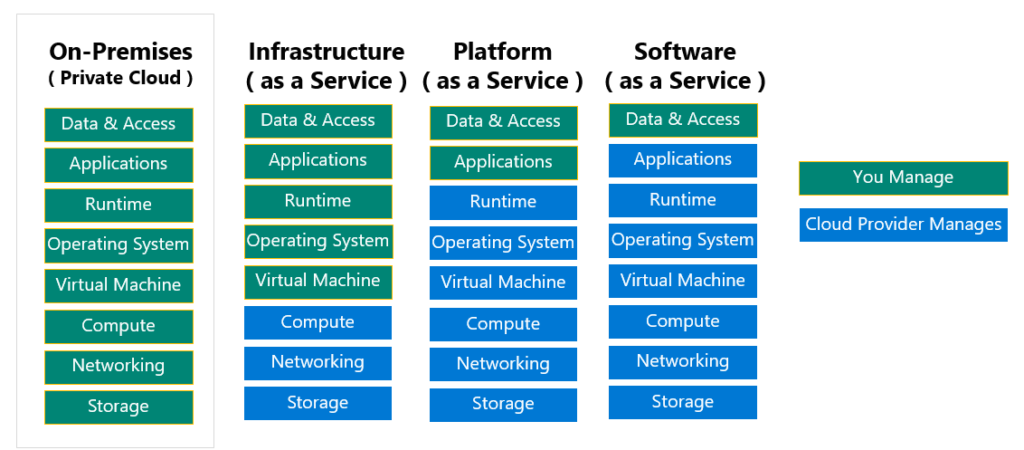
Shared responsibility model
Learn and SkillPipe content:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is one of the fundamental cloud computing service models that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. In an IaaS model, cloud providers deliver and manage essential IT infrastructure components, such as servers, storage, networking, and virtualization, to customers on a pay-as-you-go basis. Customers can access and use these resources without the need to invest in and maintain physical hardware, reducing the burden of managing on-premises infrastructure.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing service model that provides a platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexities of managing underlying infrastructure and software components. In essence, PaaS abstracts the infrastructure layer and offers a set of tools, services, and development frameworks that facilitate application development and deployment.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing service model that delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. In the SaaS model, software applications are hosted and maintained by a cloud service provider, and users access these applications through web browsers or dedicated client applications. SaaS eliminates the need for users to install, maintain, or manage the software locally on their devices, as everything is managed and maintained by the SaaS provider.
Learn and SkillPipe content:
Other links:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/courses/az-900t00


Great and clear explanations of the Cloud